Let’s get one thing clear up front. I don’t like working from home. I don’t even particularly care for the idea of working from home. There are many who think that it is the absolute best idea since sliced bread, but I am not one of those. Yet it seems that situations and events have conspired in such a way that I now find myself working from home. However, it is pretty clear to me that when I take all things into account, that working at home is the best alternative for me right now. I’ll talk about the things that I have learned that I need to do to be as effective as possible in working from home.
I guess I may just be a creature of habit, but I have always “gone” to work. You know. Got up. Cleaned up. Went to the office. Just like I had “gone” to school. I didn’t “go to school” at home. I went to the then appropriate institution of learning.
This was back in a time before technology enabled “working from home”. In fact, it was not uncommon for people to have to relocate to different cities if their responsibilities changed, and they found themselves with a job in another location. This was what is now referred to as “the dark ages”….
Back then teams were not virtual. People actually had to be in the same place in order to work together. True synergies were achieved because everyone was in the same room when a meeting occurred. It was a time when process was not as dominant as it is now. Individual knowledge, experience and judgement were sought after to create the most effective team dynamic. It was all about finding the best and most efficient way to achieve the desired goal.
But I have digressed in my remembrances of those bygone times.
Times have changed. Companies now get merged and purchased with significantly increased regularity. The pendulum of workplace office arrangements has swung from the highly structured shared office environments of the 1950’s (where everybody had an assigned workspace within the shared space) to the cube farms (where everyone had there own individual work space and everyone measured their progress by cube square footage and wall height) of the 1980’s and 1990’s, to the current iteration of the 1950’s model where no one has an assigned work space, but they all work together in the shared environment, and you have to put everything away in your locker at the end of the day.
The last time I had to have a locker to put my things away in at the end of the day was when I was back in school.
Against this backdrop of office moves, business consolidation and “new and improved” office environments, should you find yourself with a pretty lengthy commute to get to a new office location, with the new shared dynamic seating environment, you might choose to give working at home a try. When I did this a few weeks ago I found out a few things that I needed to do to help with my effectiveness, even though I was no longer in my preferred working environment.
I also recalled several Dilbert ® cartoons by Scott Adams. I like to follow him because he appears to be scarily prescient when it comes to most interesting work topics. It shouldn’t surprise anyone that he has been addressing the work at home topic for over thirty years. Talk about being ahead of your time.
As I mentioned earlier, part of going to work was the process of getting ready for work. The getting up and cleaning up. I am an early to the office person. Since I have worked with several groups internationally in the past, I got it the habit of coming into the office early in order to facilitate communications with them. If I didn’t have calls or meetings scheduled early, I used the early quiet time to get a jump on the requirements of the day.
I also liked the idea that for the most part, my working time and my personal time had two fairly specific delineators; namely the commute to and from the office. There was a defined “starting time” when I got to the office, and a defined “ending time” when I left the office. Obviously, there were situations where calls, meetings and work would and could cross these thresholds, but for the most part, there was a beginning and an end to the work day.
When working at home the “start” and “stop” lines seem to begin to blur. There is no longer is any appreciable commute to the office. You can get up and walk into the home office and just start working. When working at home it is easy to say that I’ll go through the preparatory activities later. The idea is that you could just get up and go into the “office” without any preparation. This didn’t work for me. I found that the “ritual” of getting up and preparing to work helped me get into the proper frame of mind to do the work I needed to do. Needless to say, Dilbert recognized this activity as well.
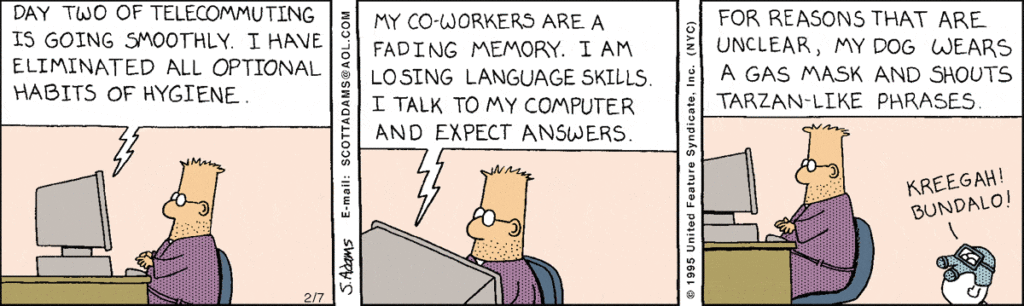
As a side note, the above comic strip is from 1995.
I also found that I worked and concentrated best in a professional environment. That meant no turning on of the television to see what was on the news. No turning on of the stereo to create background music. These are distractions that do not normally exist within the business environment, and if you are going to extend the business environment to the work at home structure, they shouldn’t exist there either.
And again, Dilbert has addressed this very issue:
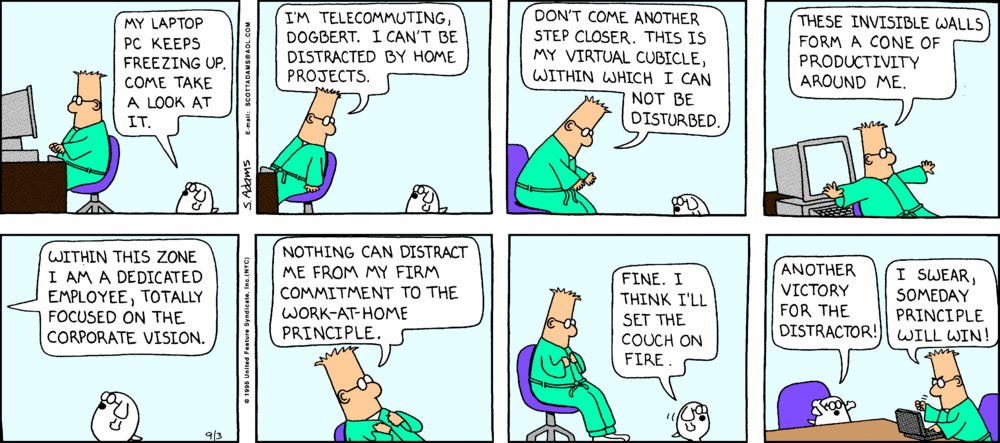
And again, this comic is from 1995.
Finally, despite all the assurances to the contrary, access to the corporate network, which is required in order to work from home to be viable, can be somewhat challenging. There are usually specific secure remote access applications that must be present and mastered in order to access the network. The issue usually arises in the form of needing access to the secure corporate network in order to request support in order to get access to the secure corporate network. There have definitely been improvements made in this area, but as I have noted, it can still be somewhat challenging.
Usually what happens here is that a trip must be made to the new office where access to the corporate network is available, in order to contact the Information technology group that is responsible for simplifying remote access to the secure network. This then ends up creating other issues since the remote access issue can no longer be replicated because you are no longer using remote access when requesting support.
The result of this interaction with the Information Technology support group is then the closure of the trouble ticket reporting the remote access issue, since the issue seems to have rectified itself by your coming into the office.
And you guessed it. Dilbert has also recognized this as an issue facing many today.

I have found that the best way for me to work at home is to make sure that I am preparing for and acting as though I am going to work in the standard office environment. Waking, preparing, dressing, etc., as though I were going into a standard business office helps me make sure that I am in the “work” mind set, as opposed to the “home” mind set. This of course is referring back to the time when home and work were indeed two separate entities.
Working at home does present its own set of unique challenges. It is almost too easy to fall into a new set of behaviors that may not be as conducive to creating a good work environment as many expected. While it is convenient, for me it doesn’t match the energy of the collocated team. I understand the value of the virtual team, but for me, it is hard to measure what was given up in exchange for what is hoped to be gained by the new.
Maybe it will just take some more time for me to get used to it.