It seems to me that too many times I have heard the words “budget” and “quota” used interchangeably. I don’t know why, but this really concerns me. Perhaps I am over reacting. It doesn’t seem to bother others. At least if it does, they aren’t showing it. Perhaps it is just my recent dealing with budget-oriented groups that are acting like quota-oriented groups that is making me more sensitive to this phenomenon. In any event, I’ll do a little comparing and contrasting of budgets and quotas and see what the rest of you think.
First,
let’s put a couple of definitions out there. It is always good for everyone to
start from the same baseline. First off, do not Google “budget”. You will get
far more than you ever wanted to know about some care rental company. But, as
you might guess, let’s start with:
Budget
Budgeting for a business is a process of expressing a detailed quantification of resource requirements (capital, material or people) that are expected for given time period in future. Budgeting can be done for any person, business, government or anything that makes and spends money. Restricting in this definition to financial results for business firms we can explain budgeting as process of preparing a detailed statement of financial results that are expected in the future period of time.
As you can see it primarily deals with the amount of money (or resources) needed or available for a purpose in a future period of time. This means it is a definition of how much you can spend on, or the expense for something. Let’s keep this “spending” idea in mind when we talk further about budgets.
Now we will move on to quotas. Hopefully this one will be a little more straight forward.
Quota
Sales Quota is the sales goal or figure set for a product line, company division or sales representative. It helps the managers to define and stimulate sales effort. Sales quota is the minimum sales goal for a set time span. Sales Quota can be individual, or group based e.g. for a business unit or a team.
Again, we have a financial goal for a future or set amount of time. Only this time it is focused on sales (orders and revenue) as income to the business, not the expenses of the business.
Now admittedly there are other definitions for both budget and quota, but these are also for utilizations of the terms for applications far outside the normal business usage. When you start discussing immigration, college acceptance and items such as those the line can become somewhat murkier. However, we will not go there, or anywhere near there today.
So here we have what I consider the crux of the issue. Budgets are associated with expenses for a set period of time and quotas are associated with sales for a period of time. This seems like a pretty simple set of definitions and differences. So why are people using them interchangeably?
I think some of my confusion may stem from the observation regarding “which side of the fence” people are speaking from. The example I will use here involves the government and everybody’s favorite topic, taxes.
For the longest time taxes were just that, taxes. Taxes were the amount that citizens paid the government. Taxes went up. Taxes went down. Periodically there was an attempt at tax reform when things go too complicated and it appeared that special interest groups were getting away with too much. By and large we all paid taxes.
But somewhere along the line this changed. From the government’s point of view (their side of the fence) taxes started to be referred to as “revenue”. Since taxes were, in the truest definition, the income that the government received, it did not seem like such a stretch or leap to go there. Soon the statement was no longer that the government was going to raise taxes (which was sure to irritate all citizens), they were going to raise revenue.
This is a much more palatable statement. Raising revenue. Everybody wants to raise revenue. Why should the government be any different? They should want to raise revenue too. The only slight difference might be that there is not another government around competing for our tax dollars. They can just vote themselves more revenue.
What doesn’t change is that from the citizen’s point of view, taxes are always an expense. Something that is paid. So, while it sounds more acceptable to raise government revenues, we need to remember that it is always raising the citizen’s expense.
This same governmental evolution occurred (in the US) when the Department of War thought it best to change its name to the Department of Defense, but that might be a discussion for a later date.
In business it appears that a similar evolution is occurring. In the past those organizations that had to live and work within budgets were called “cost centers”. They were associated with costs and expenditures. As such they were occasionally subject to reductions as most companies seemed to think that reducing costs was always a good idea.
It only goes to assume that these cost centers started to realize that the business’s expense budget was their revenue. This quantity was how much money was going to come into their piece of the business.
This was a master stroke.
No one ever wants to cut a revenue. They will cut, hack, chop and slash budgets all day long, but they will steadfastly refuse to cut a revenue.
I also think that some of the issue stems from business’s drive to remove as much overhead, or indirect cost from the business as is possible. There are essentially two way to do this. One is to actually reduce the number of resources associated with these indirect functions. The other is to try and translate these indirect cost functions into direct cost functions.
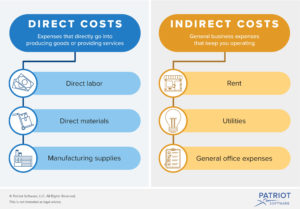
Below is a refresher on the difference between direct and indirect costs:
“The essential difference between direct costs and indirect costs is that only direct costs can be traced to specific cost objects.
A cost object is something for which a cost is compiled, such as a product, service, customer, project, or activity. These costs are usually only classified as direct or indirect costs if they are for production activities, not for administrative activities (which are considered period costs).
Examples of direct costs are direct labor, direct materials, commissions, piece rate wages, and manufacturing supplies. Examples of indirect costs are production supervision salaries, quality control costs, insurance, and depreciation.
Direct costs tend to be variable costs, while indirect costs are more likely to be either fixed costs or period costs.”
The idea here is that when everything is associated with direct costs, everything is now directly associated with the sale and the generation of revenue. When that happens, almost all of those cost justifications for those groups now get aligned with sales and more importantly sales quotas. Now all budgets for those groups are supposedly aligned with sales, which in turn are aligned with, you guessed it, quotas.
And everybody likes to achieve their quotas.
In this way what were once cost centers have now aligned themselves with the sales function. Likewise, budgets which were once limits that were not to be exceeded became quotas that were to be achieved. This is a subtle but important difference.
Beating a budget meant that you came in with an expense that was lower than the budget. Success was reducing expenses below the targeted level. Efficiency and cost reduction were key targets. In short, the costs associated with the process were separated from the sales and prices associated with the process.
By now aligning everything with the sales and revenue process, costs now in effect do become quotas.
If sales do not achieve its quota, well then obviously costs will not be affected as they have a set cost quota. As long as they are on target for their quota of costs, they are achieving their goal, regardless of what the overall profitability of the process appears to be. This engenders a strange situation.
These cost groups are now of the opinion that as long as there is cost “quota” left to spend, they have the right to continue to spend it, regardless of sales performance. It in effect becomes the sales function’s responsibility to bring sales back into alignment with the sales quotas, instead of the cost function’s responsibility to bring cost “quotas” back into alignment with the sales function’s performance.
Costs “quotas” are really nothing more than verbal sophistry.
As business continues to look for ways to improve, some of the age-old axioms still do apply. Its always a good thing to achieve or exceed sales quotas. Cost budgets are an upper limit. It is always a good thing to “come in under budget” and return unused budgets back to the business in the form of bottom line profits. And, if you hear someone claiming that they are on target to achieve their cost quota, either they are not trying hard enough, or their cost “quota” needs to be reduced.